Lycopene is found in a variety of fruits, offering an array of antioxidant carotenoid benefits
03/17/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
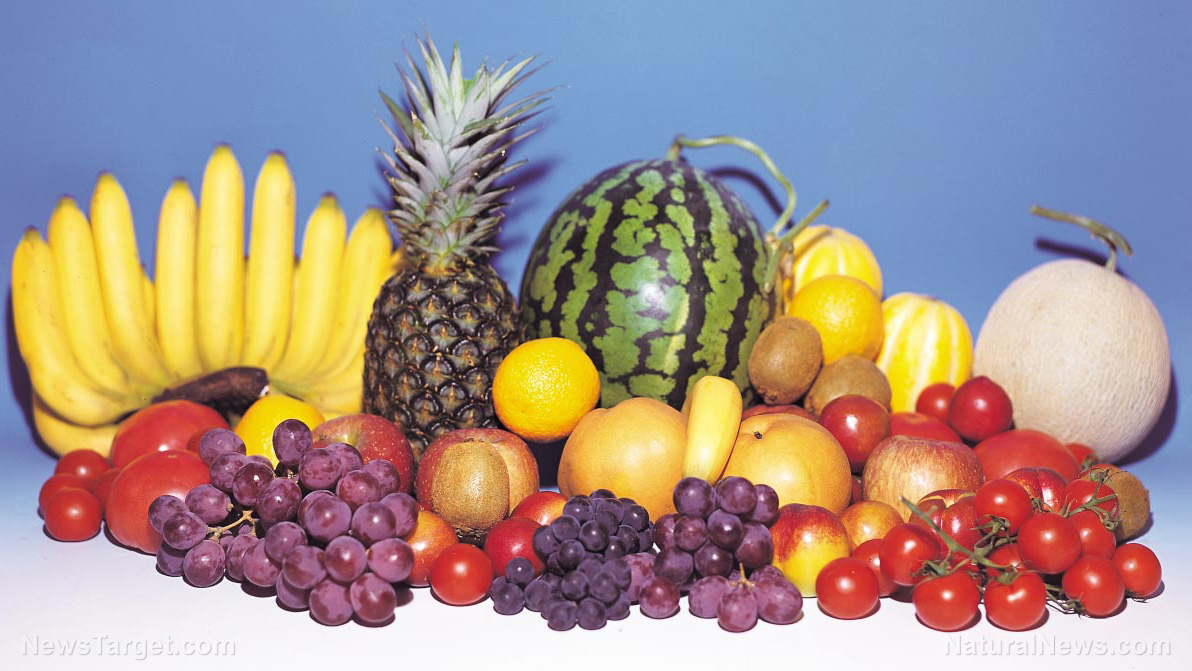

Lycopene, a compound that occurs in a variety of fruits, provides antioxidant carotenoid benefits, according to a study published in the journal Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia.
The study looked at the lycopene content of various fresh fruits, which included tomatoes, watermelons, jackfruits, bananas, grapes, oranges, and papayas. The researcher from Kalasin University in Thailand extracted lycopene from the fresh fruits with the use of a mixture of hexane, ethanol, and acetone.
Results showed that watermelons contained the highest amount of lycopene, followed by tomatoes, papayas, bananas, oranges, grapes, and jackfruits, respectively. The researcher concluded that lycopene is an essential antioxidant that can be found in red-colored fruits. In addition, the compound is said to prevent cancer and heart disease. (Related: The Antioxidant Lycopene Is Effective Against Colon Cancer.)
Lycopene and its health benefits
Lycopene plays an important role in maintaining a healthy body and mind. For one, it is a carotenoid, which is an organic pigment that can be converted into vitamin A. It is also a phytonutrient, which means that it contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Add more lycopene-rich foods to your regular diet to reap its benefits:
- Improves skin health – Studies have shown that the consumption of foods rich in lycopene, together with the use of sunscreens, can lessen skin damage caused by UVA and UVB exposure. Moreover, lycopene, when converted into vitamin A, can slow down the progression of aging as it enhances the production of collagen and melatonin, which regulate the overall health of the skin. In addition, lycopene may reduce skin redness and soothe rough skin, as it promotes the growth of new skin cells. It can also reduce skin darkening and age spots.
- Supports hair health – Hair loss, particularly in men, is associated with excess dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Regular consumption of foods rich in lycopene can help reduce excess DHT from the body, which can slow down the process of hair loss and male pattern balding. In addition, it can also promote the growth of healthy hair.
- Prevents heart disease – Heart disease is frequently associated with the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the body. A good way to fight heart disease is to eat lycopene-rich foods regularly in order to prevent the oxidation of LDL or bad cholesterol, which prevents the clogging of the arteries.
- Fights cancers – One of the cancers that lycopene can help prevent is prostate cancer, which belongs to the top three cancers in men. For cancer patients that will undergo prostate removal, a lycopene-rich diet is prescribed two to three weeks before the surgery. The diet will reduce and control cancer remission and cancer cell proliferation. Other cancers that lycopene can help fight are cancers of the breast, skin, liver, and lungs.
- Helps treat infertility – Studies show that there is a high correlation between regular consumption of lycopene-rich foods and increased sperm count among men. However, research on the effects of lycopene in treating infertility among men is still being conducted.
- Improves symptoms of diabetes – Lycopene has been found to reduce blood glucose levels as well as oxidative stress due to its antioxidant properties, which may be beneficial in managing Type 2 diabetes.
- Prevents macular degeneration – Macular degeneration, a condition that causes a gradual loss of vision in the center of the visual feed, is one of the most common causes of blindness worldwide. This can be prevented by including lycopene-rich foods in your diet because having a healthy dose of retinol or vitamin A helps maintain overall eye health.
- Fights osteoporosis – Recent studies revealed that adhering to a lycopene-rich diet helps prevent brittleness and thinness of bones, which are the main causes of osteoporosis.
If you’d like to read more news stories and studies on the health benefits of fruits, go to Fruits.news.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SUPER FOODS NEWS